Synchronization schedule
The synchronization schedule for a family defines when replicas
in the family send and receive updates. The schedule is affected by many factors,
including the rate of development at different sites, the connections among
sites, and whether you use MultiSite as
a backup strategy.
Consider the following issues when planning your synchronization strategy:
- Rate of development
If you schedule synchronizations frequently, you lose less work if a replica is deleted accidentally and you must restore it from backup.
Make sure that synchronizations do not overlap with backups.
- Time zone differences
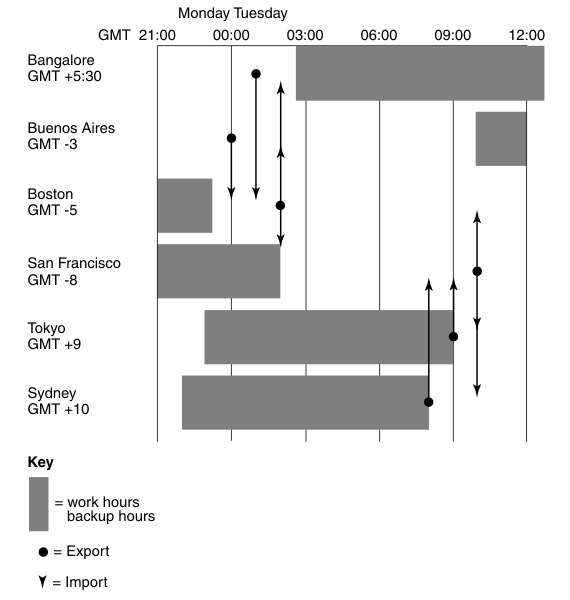
Take different time zones into account when you send an update or set up automated updates. Figure 1 illustrates synchronization among replicas in multiple time zones.
- Changes that affect both the schema repository and the
user database
Many changes are recorded in the schema repository and the user database, and oplog entries are created in both operation logs. Synchronize your schema repositories first, and then synchronize the user databases.
For example, the administrators for the family in Figure 2 in the Synchronization pattern topic make the following
decisions:
- The hub replicas, which undergo rapid development, synchronize every hour.
- Each hub replica synchronizes daily with its spoke replicas. Each spoke replica sends an update packet to the hub replica, and then the hub replica sends update packets back to the spoke replicas. Because these packets may be large and take a long time to import, the synchronization must not take place during working hours or during backups.
- All replica hosts use receipt handlers to import packets as soon as they are received.
Figure 1 shows the synchronization timeline for
the hub-spoke updates (but not the hourly hub-to-hub updates). This timeline accounts for time zone
differences and includes extra time to make sure that each synchronization phase completes before
another begins.
Figure 1. A synchronization schedule